![]() Dust mites can be found in most homes near coastal Australia. They are small and most people do not notice them unless they crawl on dark surfaces. However once seen, there may appear to be many as people go looking for them. Dust mites eat protein such as shed human skin. They are more likely to build up in numbers where people spend time on surfaces that are not smooth – such as in bed, on upholstered furniture etc – and other places where human skin can be found such as soft toys, combs and brushes.
Dust mites can be found in most homes near coastal Australia. They are small and most people do not notice them unless they crawl on dark surfaces. However once seen, there may appear to be many as people go looking for them. Dust mites eat protein such as shed human skin. They are more likely to build up in numbers where people spend time on surfaces that are not smooth – such as in bed, on upholstered furniture etc – and other places where human skin can be found such as soft toys, combs and brushes.
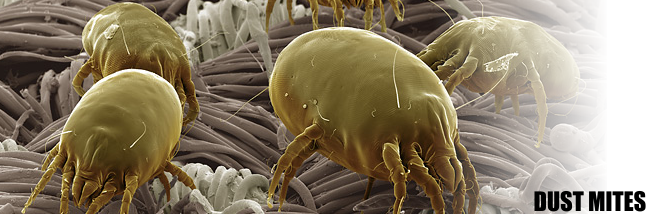 Dust mites are not considered a pest by most people – although some people are sensitive to their live dust mites, their faeces and cast skins and may suffer an allergic reaction when numbers build up. Dust mites are hard to eliminate from a property and management to keep them at low levels is mainly by lowering humidity to below 60% (if possible), exclusion (eg appropriate mattress covers) and reduction of suitable places for them to live and breed (eg carpet).
Dust mites are not considered a pest by most people – although some people are sensitive to their live dust mites, their faeces and cast skins and may suffer an allergic reaction when numbers build up. Dust mites are hard to eliminate from a property and management to keep them at low levels is mainly by lowering humidity to below 60% (if possible), exclusion (eg appropriate mattress covers) and reduction of suitable places for them to live and breed (eg carpet).
Pest management treatments can aid in the short-term reduction of dust mites but the long-term minimization of dust mites at a property requires the combination of many strategies. These strategies have several factors in common:
– reducing humidity,
– reducing ‘non-smooth’ surfaces such as carpet,
– encasing mattresses and pillows
– washing items including bed linen and soft toys regularly in hot water or water containing essential oils and
– regular, thorough cleaning and vacuuming.
